Things Nobody Tells You About The Glutathione Benefits And Your Immune System
What are the glutathione benefits? It may be the most important molecule you need to stay healthy and prevent disease.
This molecule has powerful anti-aging properties, can fight cancer, heart disease, dementia, and other chronic diseases.
It’s also important for treating everything from autism and Alzheimer’s disease and more.
What Is Glutathione And What Does it Do?
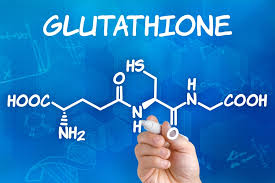 It is our body that naturally produces glutathione, a combination of three simple building blocks of protein or amino acids − cysteine, glycine, and glutamine.
It is our body that naturally produces glutathione, a combination of three simple building blocks of protein or amino acids − cysteine, glycine, and glutamine.
Glutathione is the master antioxidant because it can regenerate itself in the liver after each “fill-up” of free radicals and go back to work.
Free radicals are often the by-product of normal cellular metabolic oxidation and toxic overload.
They can lead to autoimmune diseases, several types of cancer, and even heart attacks.
Keeping yourself healthy, boosting your performance, preventing disease, and aging well all depend on keeping glutathione levels high.
It is critical for immune function and controlling inflammation.
It is the master detoxifier and the body’s main antioxidant, protecting our cells and making our energy metabolism run well.
Research has shown that raised glutathione levels decrease muscle damage, reduce recovery time, increase strength and endurance, and shift metabolism from fat production to muscle development.
Glutathione is critical in helping the body’s first line of defense against disease and illness – the immune system − do its job of fighting infections.
Among other glutathione benefits are, it further supports the immune system in preventing cancer and other illnesses. Studies have also shown that glutathione can help in the treatment of AIDS.
Studies have also shown that glutathione can be effective in treating fatty liver disease, both alcoholic and non-alcoholic. It’s especially effective for people who make healthy lifestyle changes.
One of the main glutathione benefits is it’s essential for maintaining healthy cellular mitochondria.
Damaged or malfunctioning cellular mitochondria are part of the cancer process.
This occurs when exposure to toxins and unhealthy cellular terrain combine to trigger a cellular defensive response.
During this process healthy cells become cancer cells by reverting to a primitive form of respiration that uses glucose (sugar) instead of oxygen for respiration.
They then refuse to die and keep multiplying.
The secret of the power of glutathione may be the sulphur chemical groups it contains.
Sulphur is a sticky, smelly molecule which helps eliminate all the bad things in the body.
Its stickiness allows it to capture damaging free radicals and toxins like mercury and other heavy metals.
As natural health author Paul Fassa wrote:
Glutathione is critical for one simple reason: It recycles antioxidants. You see, dealing with free radicals is like handing off a hot potato.
The free radicals move around from vitamin C to vitamin E to lipoic acid and then finally to glutathione which cools off the free radicals and recycles other antioxidants.
After this happens, the body can “reduce” or regenerate another protective glutathione molecule and we are back in business.”
Dr. Mark Hyman calls glutathione the “mother of all antioxidants” and says that he has found glutathione deficiency to be common in virtually all seriously ill patients he has treated.
This includes people with chronic fatigue syndrome, heart disease, cancer, chronic infections, autoimmune disease, diabetes, autism, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, arthritis, asthma, kidney problems, liver disease, and more.
Glutathione Deficiency
The body forms glutathione naturally, but production decreases as we age. Toxins also decrease healthy glutathione levels.
If you are sick, feeling old, or just not in peak shape, you likely have a glutathione deficiency.
The esteemed British medical journal, The Lancet, found the highest glutathione levels in healthy young people, lower levels in healthy elderly, lower still in sick elderly, and the lowest of all in the hospitalized elderly.
Normally, the body recycles glutathione − except when the toxic load becomes too great.
When glutathione becomes depleted it can no longer protect against free radicals, infections, or cancer, and we can’t get rid of toxins.
This leads to further sickness and soon we are in the downward spiral of chronic illness.
Active Glutathione is Defined as GSH
Glutathione becomes inactive when it becomes saturated from doing its work of collecting free radicals, but it tends to regenerate itself in a healthy liver.
Under ideal conditions, 10% of the glutathione remains inactive (or oxidized), while the other 90% is active.
As the active glutathione (also known as GSH), drops below 90% and allows the inactive to increase beyond 10%, the struggle for optimum health begins to become a losing battle.
When toxins build up, the GSH diminishes even more. When GSH falls below 70%, the immune system becomes critically compromised.
Foods & Supplements that Increase Glutathione Levels in Your Body
Certain foods contain precursors to help the liver produce more glutathione.
These include sulphur-rich foods such as garlic, onions, and cruciferous vegetables (i.e. broccoli, kale, collards, cabbage, cauliflower and watercress), premium bioactive whey products, and colostrum.
You can also increase glutathione by increasing your vitamin C intake or adding milk thistle or turmeric to your diet.
Precursors must be employed to boost your liver’s ability to create healthy glutathione levels
This is because supplemental glutathione has issues with getting through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract intact without being degraded.
Exercise boosts glutathione levels and helps boost your immune system, improve detoxification, and enhance your body’s own antioxidant defenses.
Start slow and build up to 30 minutes a day of vigorous aerobic exercise like walking or jogging, or play various sports. Strength training for 20 minutes, three times a week is also helpful.
Other supplements which can help increase healthy glutathione levels and maximize glutathione benefits include:
- A good all-around organic, whole-food derived nutritional supplement.
- N-acetyl-cysteine (NAC) helps boosting glutathione. Time release NAC is the best option for keeping levels high throughout the day.
- Methylation nutrients, including folate, vitamin B6, and vitamin B12 are critical to keep the body producing and recycling glutathione.
- Selenium helps the body recycle and produce more glutathione.
- The family of antioxidants which includes vitamins C and E (in the form of mixed tocopherols) work together to recycle glutathione
- Milk thistle (silymarin) helps increase glutathione levels and is famed for its ability to cleanse, protect, and regenerate the liver.
It is also worth noting that alpha-lipoic acid is a close second to glutathione in terms of importance for our cells.
It is crucial for energy production, blood sugar control, brain health, and detoxification.
Glutathione benefits are handsome and Glutathione is one of the body’s most important and potent antioxidants.
Antioxidants are substances that reduce oxidative stress by combating free radicals in the body.
While the foods you eat have most antioxidants, it is your body that produces glutathione.
Three amino acids such as glutamine, glycine and cysteine are the primary components of glutathione.
There are a number of reasons why your body’s glutathione level may become depleted, including poor diet, chronic disease, infection and constant stress.
Glutathione drops in levels as we age.
Maintaining adequate levels of this antioxidant is incredibly important. Below are 10 of the best ways to increase your glutathione levels naturally.
1. Consume Sulfur-Rich Foods
Sulphur is an important mineral that occurs naturally in some plant and protein foods.
It’s a co-factor for the structure and activity of important proteins and enzymes in the body. Notably, sulphur must be available for the synthesis of glutathione.
Sulphur is in two amino acids in food: methionine and cysteine. Dietary proteins, such as beef, fish and poultry primarily provide this key trace element.
However, there are vegetarian sources of sulphur as well…
…such as cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower, kale, watercress and mustard greens.
A number of human and animal studies have found that eating sulphur-rich vegetables may reduce oxidative stress by increasing glutathione levels.
Allium vegetables, including garlic, shallots and onions, also boost glutathione levels — likely due to their sulphur-containing compounds.
2. Increase Your Vitamin C Intake
A variety of foods, particularly fruits and vegetables provide vitamin C which is a water-soluble vitamin.
Strawberries, citrus fruits, papayas, kiwis and bell peppers are all examples of foods rich in vitamin C.
This vitamin has many functions, including working as an antioxidant to protect cells from oxidative damage. It also maintains the body’s supply of other antioxidants, including glutathione.
Researchers have discovered that vitamin C may help increase glutathione levels by attacking free radicals first, thereby sparing glutathione.
They also found that vitamin C helps reprocess glutathione by converting oxidized glutathione back to its active form.
In fact, researchers have found that taking vitamin C supplements increased glutathione levels in white blood cells in healthy adults.
In one study, adults took 500–1,000 mg of vitamin C daily for 13 weeks, leading to an 18% increase of glutathione in white blood cells.
Another study showed that taking 500 mg of vitamin C supplements per day increased glutathione in red blood cells by 47%.
However, these studies involved vitamin C supplements. Given that supplements are concentrated versions of the vitamin, it’s unclear if foods would have the same effect.
Further research in future will determine if you can increase glutathione levels by eating foods containing vitamin C.
3. Add Selenium-Rich Foods to Your Diet to Maximize Glutathione Benefits
Selenium is an essential mineral and a glutathione co-factor, meaning it’s an essential substance that promotes glutathione activity and maximizes glutathione benefits.
Some of the best sources of selenium are beef, chicken, fish, organ meats, cottage cheese, brown rice and Brazil nuts.
By increasing your intake of selenium, you may help maintain or increase your body’s supply of glutathione.
The official Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for selenium for adults is 55 mcg but in reality it should be at least 500 mcg per day to avoid any cardiomyopathy issues. This is based on the amount needed to maximize the production of glutathione peroxidase.
One study investigated the effects of selenium supplements in 45 adults with chronic kidney disease. All of them received 200 mcg of selenium daily for three months.
Interestingly, all of their glutathione peroxidase levels increased significantly
Another study showed that taking selenium supplements increased glutathione peroxidase levels in patients on haemodialysis.
Again, the above studies involved supplements, rather than selenium-rich foods.
Additionally, we must consider that the tolerable upper intake level (UL) is set at 600 mcg per day. Due to possible toxicity, be sure to discuss selenium supplements and dosage with your health care provider.
For most healthy adults, eating a balanced diet with selenium-rich foods will ensure adequate levels of selenium — and, therefore, healthy glutathione levels.
4. Eat Foods Naturally Rich in Glutathione
The human body produces glutathione, but there are also dietary sources. Spinach, avocados, asparagus and okra are some of the richest dietary sources.
However, dietary glutathione is poorly absorbed by the human body. Additionally, cooking and storage conditions can decrease the amount of glutathione found in food.
Despite having a lower impact on increasing glutathione levels, glutathione-rich foods may help decrease oxidative stress.
For example, a non-experimental study showed that…
…people who consumed the most glutathione-rich foods had a lower risk of developing mouth cancer.
Ultimately, further research is going to be key to fully understand the effect of glutathione-rich foods on oxidative stress and glutathione levels.
5. Supplement With Organic Whey Protein
Your body’s production of glutathione depends on certain amino acids.
An amino acid called cysteine is a particularly important amino acid that is involved in glutathione synthesis.
Foods rich in cysteine, such as whey protein, may increase your glutathione supply.
In fact, research strongly supports this claim, as many studies have found that organic whey protein may increase levels of glutathione and, therefore, reduce oxidative stress.
6. Consider Milk Thistle To Preserve Glutathione Benefits
Milk thistle supplements are another way to boost glutathione levels naturally.
This herbal supplement is extracted from the milk thistle plant, known as Silybum marianum.
Milk thistle is comprised of three active compounds, collectively known as silymarin.
Silymarin is found in high concentrations in milk thistle extract and is well known for its antioxidant properties.
Furthermore, silymarin has been shown to increase glutathione levels and prevent depletion in both test-tube and rodent studies.
Researchers believe that silymarin is able to maintain glutathione levels by preventing cell damage.
7. Try Turmeric Extract To Boost Glutathione Benefits By Increasing Its Level
Turmeric is a vibrant yellow-orange herb and a popular spice in Indian cuisine.
The herb has been used medicinally in India since ancient times. The medicinal properties of turmeric are likely linked to its main component, curcumin.
The curcumin content is much more concentrated in the extract form of turmeric, compared to the spice.
Numerous animal and test-tube studies have shown that…
…turmeric and curcumin extract have the ability to increase glutathione levels.
Researchers conclude that the curcumin found in turmeric may assist in restoring adequate levels of glutathione and improve the activity of glutathione enzymes.
To experience an increase in glutathione levels, you would need to take turmeric extract, as it would be extremely difficult to consume the same levels of curcumin with turmeric spice.
8. Get Enough Sleep For Maintaining The Anti-Oxidant Glutathione Benefits
A good night’s rest is essential for overall health. Interestingly, long-term lack of sleep can cause oxidative stress and even hormone imbalances
Furthermore, research has shown that chronic lack of sleep may decrease glutathione levels.
For example, a study measuring glutathione levels in 30 healthy people and 30 people with insomnia found that glutathione peroxidase activity was significantly lower in those with insomnia.
Multiple animal studies have also shown that sleep deprivation causes a decrease in glutathione levels
Therefore, making sure you get good, restorative sleep each night may help maintain or boost your levels of this antioxidant.
9. Exercise Regularly To Maximize Glutathione Benefits
Regular physical activity has long been recommended by physicians and healthcare providers. It’s no surprise that exercise is good for both your physical and mental health.
Recent research shows that exercise is also helpful in maintaining or increasing antioxidant levels, especially glutathione.
Completing a combination of both cardio and circuit weight training increases glutathione the most, compared to completing cardio or weight training alone.
However, athletes who over train without maintaining adequate nutrition and rest may be at risk of decreased glutathione production and losing glutathione benefits.
Therefore, be sure to incorporate physical activity into your regular routine in a gradual and sensible way.
10. Avoid Drinking Too Much Alcohol
It’s no surprise that many adverse health effects are associated with chronic and excessive alcohol intake.
Alcoholism is commonly associated with ailments such as liver cirrhosis, brain damage and pancreatitis.
While not as well known, lung damage is also an adverse effect of alcoholism. This is likely related to a depletion of glutathione levels in the lungs.
The small airways of the lungs require glutathione to function properly
In fact, healthy lungs have up to 1,000 times more glutathione than other parts of the body.
Depletion of glutathione in the lungs of alcoholics is most likely due to oxidative stress caused by chronic alcohol use.
Research has identified an 80–90% decrease in lung glutathione levels in those who regularly consume excessive amounts of alcohol.
Thus, limiting your alcohol intake may help you maintain healthy glutathione levels.
The Bottom Line of Glutathione Benefits
One of the main glutathione benefits is it’s an important antioxidant that is primarily made by the body, but is also found in dietary sources.
Unfortunately, many factors, such as aging, a poor diet and a sedentary lifestyle will deplete your levels of this antioxidants.
Luckily, you can maintain appropriate glutathione levels by increasing your physical activity, avoiding drinking too much alcohol, getting enough sleep and eating a balanced diet.
Taking milk thistle, turmeric or whey protein supplements may also help boost your levels, therefore maximizing glutathione benefits.
At the end of the day, there are many simple and natural ways you can increase your levels of this important and potent antioxidant.